Third Battle of Kharkov
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
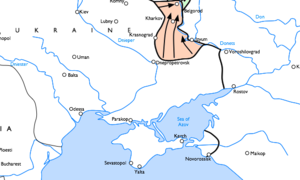
The Third Battle of Kharkov was a series of offensive operations on the Eastern Front of World War II, undertaken by the German Army Group South against the Red Army, around the city of Kharkov (Russian: Харьков; Ukrainian: Харків), between 19 February and 15 March 1943. Known to the Germans as the Donets Campaign, and to the Soviets as the Donbas and Kharkov operations, the German counterstrike led to the destruction of approximately 52 Soviet divisions and the recapture of the cities of Kharkov and Belgorod.
As the German Sixth Army was encircled in Stalingrad, the Red Army undertook a series of wider offensives against the rest of Army Group South. These culminated on 2 January 1943, when the Soviets launched Operation Star, which between January and early February broke German defenses and led to the Soviet recapture of Kharkov, Belgorod and Kursk. The Soviet offensive was successful, but caused participating Soviet units to over-extend themselves. Freed on 2 February by the surrender of the German Sixth Army, the Red Army's Central Front turned its attention west and on 25 February expanded its offensive against both Army Group South and Army Group Center. However, months of continuous operations had taken a heavy toll on the Soviets and some divisions were reduced to 1,000–2,000 combat effective soldiers. On 19 February, Field Marshal Erich von Manstein took the opportunity to launch his Kharkov counterstrike, using the fresh SS Panzer Corps and two panzer armies.
Although the Germans were also understrength, the Wehrmacht successfully flanked, encircled and defeated the Red Army's armored spearheads south of Kharkov. This enabled von Manstein to renew his offensive against the city of Kharkov proper, which began on 7 March. Despite orders to encircle Kharkov from the north, the SS Panzer Corps instead decided to directly engage Kharkov on 11 March. This led to four days of house-to-house fighting before Kharkov was finally recaptured by the 1st SS Panzer ("Leibstandarte") Division on 15 March. Two days later, the Germans also recaptured Belgorod, creating the salient which in July 1943 would lead to the Battle of Kursk. The German offensive cost the Red Army an estimated 70,000 casualties but the house-to-house fighting in Kharkov was also particularly bloody for the German SS Panzer Corps, which had lost approximately 4,300 men by the time operations ended in late March.
Contents |
Background
At the start of 1943, the German Wehrmacht faced a major crisis[4] as Soviet forces encircled and reduced the German Sixth Army at Stalingrad and expanded their Winter Campaign towards the Don River.[5] On 2 February 1943 the Sixth Army's commanding officers surrendered, and an estimated 90,000 men were captured by the Red Army.[5][6] Total German losses at the Battle of Stalingrad, excluding prisoners, were between 120,000[7] and 150,000.[5] Throughout 1942 German casualties totaled around 1.9 million personnel,[8] and by the start of 1943 the Wehrmacht was around 470,000 men below full strength on the Eastern Front.[9] At the beginning of Operation Barbarossa, the Wehrmacht was equipped with around 3,300 tanks;[10] by 23 January only 495, mostly of older types, remained operational along the entire length of the German–Soviet front.[11] Emboldened by their victory at Stalingrad the Red Army launched an offensive towards the Donets River, west of the Don,[12] with the objective of destroying German forces in the area.[13]
On 2 February, the Red Army launched Operation Star, threatening to recapture the cities of Belgorod, Kharkov and Kursk.[14] A Soviet drive, spearheaded by four tank corps organized under Lieutenant-General Markian Popov, pierced the German front by crossing the Donets River and pressing into the German rear.[15] On 15 February, two fresh Soviet tank corps threatened the city of Zaporizhia on the Dnieper River, which controlled the last major road to Rostov and housed the headquarters of Army Group South and Luftflotte 4 (Air Fleet Four).[16] Elsewhere, despite Hitler's orders to hold the city, Kharkov was abandoned by German forces and the city was recaptured by the Red Army on 16 February.[17] Hitler immediately flew to von Manstein's headquarters at Zaporizhia. Von Manstein informed him that an immediate counterattack on Kharkov would be fruitless, but that he could successfully attack the overextended Soviet flank with his five Panzer Corps, and recapture Kharkov later.[18] On 19 February Soviet armoured units broke through the German lines and approached the city. Hitler departed while the Soviets were only some thirty kilometres away from the airfield.[19] In view of the worsening situation Hitler gave Manstein operational freedom.

The surrender of the German Sixth Army at Stalingrad freed six Soviet armies, under the command of Konstantin Rokossovsky, which were refitted and reinforced by the 2nd Tank Army and the 70th Army.[20] These forces were repositioned between the junction of German Army Groups Center and South.[21] Known to the Soviets as the Kharkov and Donbas operations,[22] the offensive sought to surround and destroy German forces in the Orel salient, cross the Desna River and surround and destroy German Army Group Center.[20] Originally planned to begin between 12–15 February, deployment problems forced the Red Army's command (Stavka) to push the start date back to 25 February.[23] Meanwhile, the Soviet 60th Army pushed the German Second Army's 4th Panzer Division away from Kursk, while the Soviet 13th Army forced the Second Panzer Army to turn on its flank. This opened a 60 kilometers (37 mi) breach between these two German forces, shortly to be exploited by Rokossovsky's offensive.[24] While the Soviet 14th and 48th Armies attacked the Second Panzer Army's right flank, making minor gains,[25] Rokossovsky launched his offensive on 25 February, breaking through German lines and threatening to surround and cut off the German Second Panzer Army and the Second Army, to the south.[26] However, unexpected German resistance began to slow the operation considerably,[25] offering Rokossovsky limited gains on the left flank of his attack and in the center.[27] Elsewhere, the Soviet 2nd Tank Army had successfully penetrated 160 kilometers (99 mi) the German rear, along the left flank of the Soviet offensive, increasing the length of the army's flank by an estimated 100 kilometers (62 mi).[28]
While the Soviet offensive continued, Field Marshal von Manstein was able to put the SS Panzer Corps — now reinforced by the 3rd SS ("Totenkopf") Division — under the command of the Fourth Panzer Army, while Hitler agreed to release seven understrength panzer and motorized divisions for the impending counteroffensive. The Fourth Air Fleet, under the command of Field Marshal Wolfram von Richthofen, was able to regroup and increase the amount of daily sorties from an average of 250 in January to 1,000 in February, providing German forces strategic air superiority.[22] On 20 February, the Red Army was perilously close to Zaporizhia, signaling the beginning of the German counterattack,[29] known to the Germans as the Donets Campaign.[30]
Comparison of forces
Between 13 January and 3 April 1943, an estimated 500,000 Red Army soldiers took part in what was known as the Voronezh–Kharkov Offensive.[1] In all, an estimated 6,100,000 Soviet soldiers were committed to the area, with another 659,000 out of action with wounds of varying severity. In comparison, the Germans could account for 2,200,000 personnel on the Eastern Front, with another 100,000 deployed in Norway. As a result, the Soviets deployed around twice as many personnel as the Wehrmacht in early February.[31] However, as a result of their over-extension and casualties taken during their offensive, at the beginning of Manstein's counterattack the Germans could achieve a tactical superiority in numbers, including the number of tanks present — for example, Manstein's 350 tanks outnumbered Soviet armor almost seven to one at the point of contact.[29]
German forces

At the time of the counterattack, Manstein could count on the Fourth Panzer Army, composed of XLVIII Panzer Corps, the SS Panzer Corps[32] and the First Panzer Army, with the XL and LVII Panzer Corps.[33] The XLVIII Panzer Corps was composed of the 6th, 11th and 17th Panzer Divisions, while the SS Panzer Corps was organized with the 1st SS Panzer ("Leibstandarte") Division and the 2nd SS Panzer ("Das Reich") Division.[32] In early February, the combined strength of the SS Panzer Corps was an estimated 20,000 soldiers. Geographically, the Fourth Panzer Army and the First Panzer Army were situated south of the Red Army's bulge into German lines; the First Panzer Army was positioned east of the Fourth Panzer Army. The SS Panzer Corps was deployed along the northern edge of the bulge, on the northern front of Army Group South.[33]
Comparatively, the Germans were able to amass around 70,000 men against the 210,000 Red Army soldiers which were earmarked for the offensive operations towards the Don River.[2] The German Wehrmacht was understrength, especially after continuous operations between June 1942 and February 1943, to the point where Hitler appointed a committee made up of Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel, Martin Bormann and Hans Lammers, to recruit 800,000 new able-bodied men — half of whom would come from "nonessential industries".[34] However, the effects of this recruitment were not seen until around May 1943, when the German armed forces were at their highest strength since the beginning of the war, with 9.5 million personnel.[35]
By the start of 1943 Germany's armored forces had sustained heavy casualties.[36] It was unusual for a Panzer Division to field more than 100 tanks, and most averaged only 70–80 serviceable tanks at any given time.[37] After the fighting around Kharkov, Heinz Guderian embarked on a program to bring Germany's mechanized forces up to strength. Despite his efforts, a German panzer division could only count on an estimated 10,000–11,000 personnel, out of an authorized strength of 13,000–17,000 soldiers.[38] Only by June did a panzer division begin to field between 100–130 tanks each.[35] SS divisions were normally in better shape, with an estimated 150 tanks, a battalion of self-propelled assault guns and enough half-tracks to motorize most of its infantry and reconnaissance soldiers[35] — these had an authorized strength of an estimated 19,000 personnel.[39] At this time, the bulk of Germany's armor was still composed of Panzer IIIs and Panzer IVs,[40] although the "Das Reich" SS Panzer Division had been outfitted with a number of Tiger I tanks.[41]
The Fourth Panzer Army was commanded by General Hermann Hoth, while the First Panzer Army fell under the leadership of General Eberhard von Mackensen.[3] The 6th, 11th and 17th Panzer Divisions were commanded by Generals von Hünersdorff,[42] Hermann Balck[43] and Fridolin von Senger und Etterlin,[44] respectively. The SS Panzer Corps was commanded by General Paul Hausser, who also had the 3rd SS Panzer (Totenkopf) Division under his command.[45]
Red Army
Since the beginning of the Red Army's exploitation of Germany's Army Group South's defenses in late January and early February, the fronts involved included the Bryansk, Voronezh and Southwestern Fronts.[33] These were under the command of Generals M. A. Reiter,[46] Filipp Golikov[3] and Nikolai Vatutin,[47] respectively. On 25 February, Marshal Rokossovsky's Central Front also joined the battle.[24] These were positioned in such a way that Reiter's Briansk Front was on the northern flank of Army Group South, while Voronezh was directly opposite of Kursk, and the Southwestern Front was located opposite their opponents.[33] Central Front was deployed between Briansk and Veronezh Fronts, to exploit the success of both of these Soviet units,[48] which had created a gap in the defenses of the German Second Panzer Army.[24] This involved an estimated 500,000 soldiers, while around 346,000 personnel were involved in the defense of Kharkov after the beginning of the German counterstroke.[1]
Like their German counterparts, Soviet divisions were also seriously understrength. For example, divisions in the 40th Army averaged 3,500–4,000 men each, while the 69th Army fielded some divisions which could only count on 1,000–1,500 soldiers. Some divisions had as little as 20–50 mortars to provide fire support. This shortage in manpower and equipment led Vatutin's Southwestern Front to request over 19,000 soldiers and 300 tanks, while it was noted that the Voronezh Front had only received 1,600 replacements since the beginning of operations in 1943.[49] By the time Manstein launched his counteroffensive, Voronezh Front had lost so much manpower and had overextended itself to the point where it could no longer offer assistance to the Southwestern Front, south of it.[50]
Manstein's counterattack
What was known to the Germans as the Donets Campaign took place between 19 February[51] and 15 March 1943.[3] Originally, Manstein foresaw a three-stage offensive. The first stage encompassed the destruction of the Soviet spearheads, which had over-extended themselves through their offensive. The second stage included the recapture of Kharkov, while the third stage was designed to attack the Soviets at Kursk, in conjunction with Army Group Center — this final stage was ultimately called off due to the advent of the Russian spring thaw (Rasputitsa) and Army Group Center's reluctance to participate.[3]
First stage: 19 February – 6 March
On 19 February, Hausser's SS Panzer Corps was ordered to strike southwards, to provide a screen for the Fourth Panzer Army's attack. Simultaneously, Army Detachment Hollidt was told to contain the continuing Soviet efforts to break through German lines.[52] The First Panzer Army was ordered to drive north in an attempt to cut off and destroy Popov's Mobile Group, using accurate intelligence on Soviet strength which allowed the Germans to pick and choose their engagements and bring about tactical numerical superiority.[53] The First and Fourth Panzer Armies were also ordered to attack the overextended Soviet 6th Army and 1st Guards Army.[52] Between 20–23 February, the Leibstandarte SS Panzer Division cut through the 6th Army's flank, eliminating the Soviet threat to the Dnieper River and successfully surrounding and destroying a number of Red Army soldiers south of the Samara River. The Das Reich SS Panzer Division advanced in a northeastern direction, while the Totenkopf SS Panzer Division was put into action on 22 February, advancing parallel to the Das Reich. These two divisions successfully cut the supply lines to the Soviet spearheads.[54] First Panzer Army was able to surround and pocket Popov's Mobile Group by 24 February, although a sizable contingent of Soviet troops managed to escape north.[55] On 22 February, alarmed by the success of the German counterattack, the Soviet Stavka ordered the Voronezh Front to shift the 3rd Tank Army and 69th Army south, in an effort to alleviate pressure on the Southwestern Front and destroy German forces in the Krasnograd area.[56]

The Red Army's 3rd Tank Army began to engage German units south of Kharkov, performing a holding action while Manstein's offensive continued.[57] By 24 February, the Germans had pulled the Panzer Grenadier (Grossdeutschland) Division off the line, leaving the 167th and 320th infantry divisions, a regiment from the Totenkopf division and elements from the Leibstandarte division to defend the Western edge of the bulge created by the Soviet offensive.[58] Between 24–27 February, the 3rd Tank Army and 69th Army continued to attack this portion of the German line, but without much success. With supporting Soviet units stretched thin, the attack began to falter.[59] On 25 February, Rokossovky's Central Front launched their offensive between the German Second and Second Panzer Armies, with encouraging results along the German flanks, but struggling to keep the same pace in the center of the attack. As the offensive progressed, the attack on the German right flank also began to stagnate in the face of increased resistance, while the attack on the left began to over-extend itself.[60]
In the face of German success against the Southwestern Front, including attempts by the Soviet 6th Army breaking out of the encirclement, Stavka ordered the Voronezh Front to relinquish control of the 3rd Tank Army to the Southwestern Front. To ease the transition, the 3rd Tank Army gave two rifle divisions to the 69th Army, and attacked south in a bid to destroy the SS Panzer Corp. However, low on fuel and ammunition after the march south, the 3rd Tank Army's offensive was postponed until 3 March.[61] Furthermore, the 3rd Tank Army was harassed and severely damaged by continuous German aerial attacks with Junkers Ju 87 Stuka dive bombers.[62] Launching its offensive on 3 March, the 3rd Tank Army's 15th Tank Corps struck into advancing units of the SS Panzer Division Totenkopf and immediately went to the defensive. Ultimately, the German SS division was able to pierce the 15th Tank Corps' lines and link up with other units of the same division advancing north, successfully encircling the Soviet tank corps.[63] The 3rd Tank Army's 12th Tank Corps was also forced on the defensive immediately, after the Totenkopf and Das Reich SS Panzer Divisions threatened to cut off the 3rd Tank Army's supply route.[64] By 5 March, the attacking 3rd Tank Army had been badly mauled, with only a small amount of men able to escape northwards, and was forced to erect a new defensive line.[64]
The destruction of Popov's Mobile Group and the 6th Army during the early stages of the German counterattack created a large gap between Soviet lines. Taking advantage of uncoordinated and piecemeal Soviet attempts to plug this gap, Manstein ordered a continuation of the offensive towards Kharkov.[65] Between 1–5 March the German Fourth Panzer Army, including the SS Panzer Corps, covered 80 kilometers (50 mi) and positioned itself only about 16 kilometers (9.9 mi) south of Kharkov.[55] By 6 March, the Leibstandarte division made a bridgehead over the Mosh River, opening the road to Kharkov.[66] The success of Manstein's counterattack forced Stavka to stop Rokossovsky's offensive.[67] The First Panzer Army was able to regain a defensive line on the Donets River, and Manstein began to plan subsequent attacks to clear Soviet units west of the Donets.[68] According to the Germans, the German counterattack had cost the Red Army an estimated 23,000 soldiers dead, along with 615 tanks and 352 artillery pieces lost.[69]
Advance towards Kharkov: 7–10 March
While Rokossovsky's Central Front continued its offensive against the German Second Army, which had by now been substantially reinforced with fresh divisions, the renewed German offensive towards Kharkov took it by surprise.[70] On 7 March, Manstein made the decision to press on towards Kharkov, despite the coming of the spring thaw. Instead of attacking east of Kharkov, however, Manstein decided to orient the attack towards the west of Kharkov and then encircle it from the north.[71] Panzer Grenadier Division Grossdeutschland had also returned to the front, and threw its weight into the attack, threatening to split the 69th Army and remnants of the 3rd Tank Army.[72] Between 8–9 March, the SS Panzer Corps completed its drive north, splitting the 69th and 40th Soviet Armies, and on 9 March it turned east to complete its encirclement. Despite attempts by the Stavka to curtail the German advance by throwing in the freshly released 19th Rifle Division and 186th Tank Brigade, the German drive continued.[73]
On 9 March, the Soviet 40th Army counterattacked against the Panzer Grenadier Division Grossdeutschland in a final attempt to restore communications with the 3rd Tank Army. This counterattack, however, was caught by the expansion of the German offensive towards Kharkov on 10 March.[74] That same day, the 4th Panzer Army issued orders to the SS Panzer Corps to take Kharkov as soon as possible, prompting Hausser to order an immediate attack on the city by three SS Panzer divisions. The "Das Reich" would come from the West, the "Leibstandarte" would attack from north, and the "Totenkopf" would provide a protective screen along the north and northwestern flanks. Despite attempts by General Hoth to order Hausser to stick to the original plan, the SS Panzer Corp's commander decided to continue with his attack on the city, although Soviet defenses forced him to postpone the attack until the next day. Manstein issued an order to continue outflanking the city, although leaving room for a potential attack on Kharkov if there was little Soviet resistance, but Hausser decided to disregard the order and continue with his own plan of attack.[71] According to von Manstein, the Army Group headquarters was forced to intervene on a number of occasions to bring the SS Panzer Corps to swing eastwards to encircle the city, instead of launching a frontal attack on Kharkov.[75]
Fight for the city: 11–15 March
Early morning 11 March, the Leibstandarte division launched a two-prong attack into northern Kharkov. The 2nd Panzergrenadier Regiment, advancing from the Northwest, split up into two columns advancing towards northern Kharkov on either side of the Belgorod-Kharkov railroad. II. Battalion, on the right side of the railroad, attacked the city's Severnyi Post district, meeting heavy resistance and advancing only to the Severenyi railway yard by the end of the day. On the opposite side of the railroad, the I Battalion struck at the district of Alexeyevka, meeting a T-34-led Soviet counterattack which drove part of the I. Battalion back out of the city. Only with aerial and artillery support, coming from Ju 87 Stukas and StuG self-propelled assault guns, were the German infantry able to battle their way back into the city. A flanking attack from the rear finally allowed the Germans to achieve a foothold in that area of the city.[76] Simultaneously, SS Panzergrenadier Regiment 1, with armor attached from a separate unit, attacked down the main road from Belgorod, fighting an immediate counterattack produced over the Kharkov airfield, coming on their left flank. Fighting their way past T-34s, this German contingent was able to lodge itself into Kharkov's northern suburbs. From the northeast, another contingent of German infantry, armor and self-propelled guns attempted to take control of the road exits to the cities of Rogan and Chuhuiv. This attack penetrated deeper into Kharkov, but low on fuel the armor was forced to entrench itself and turn to the defensive.[77]

The Das Reich division attacked, on the same day, the west side of Kharkov. After penetrating into the city's Zalyutino district, the advance was stopped by a deep anti-tank ditch, lined with Soviet defenders, including anti-tank guns. A Soviet counterattack was repulsed after a bloody firefight. A detachment of the division fought its way to the southern approaches of the city, cutting off the road to Merefa. At around 3:00 pm, Hoth — Fourth Panzer Army commander — ordered Hausser to immediately disengage with Das Reich, and instead redeploy to cut off escaping Soviet troops. Instead, Hausser sent a detachment from the Totenkopf division for this task and informed Hoth that the risk of disengaging with Das Reich was far too great. On the night of 11–12 March, a breakthrough element crossed the anti-tank ditch, taking the Soviet defenders by surprise, and opening a path for tanks to cross. This allowed Das Reich to advance to the Kharkov main railway station, which would be the farthest this division would advance into the city. Hoth repeated his order at 1:15 am, of 12 March, and Hausser replied as he had replied on 11 March. However, a third attempt by Hoth was obeyed, and Das Reich disengaged, using a corridor opened by Leibstandarte to cross northern Kharkov and redeploy east of the city.[78]
On 12 March, the Leibstandarte division made progress into the city's center, breaking through the staunch Soviet defenses in the northern suburbs and began a house to house fight towards the center. By the end of the day, the division had reached a position just two blocks north of Dzerzhinsky Square.[79] The 2nd Panzergrenadier Regiment's II. Battalion was able to surround the square, after taking heavy casualties from Soviet snipers and other defenders, by the evening of 12 March. When taken, the square was renamed "Platz der Leibstandarte".[80] That night, 2nd Panzergrenadier Regiment's III. Battalion, under the command of Joachim Peiper linked up with II. Battalion in Dzerzhinsky Square and attacked southwards, crossing the Kharkov River and creating a bridgehead, opening the road to Moscow Avenue. Meanwhile, the division's left wing reached the junction of the Volchansk and Chuhuiv exit roads and went on the defensive, fighting off a number of Soviet counterattacks.[81]
The next day, Leibstandarte struck south towards the Kharkov River and Peiper's bridgehead, clearing Soviet resistance block by block. In a bid to trap the city's defenders in the center, I. Battalion of the 1st SS Panzergrenadier Regiment re-entered the city using the Volchansk exit road. At the same time, Peiper's forces were able to breakout south, suffering from bitter fighting against a tenacious Soviet defense, and link up with the division's left wing at the Volchansk and Chuhuiv road junction. Although the majority of Das Reich had, by now, disengaged from the city, a single Panzergrenadier Regiment remained to clear the southwestern corner of the city, eliminating resistance by the end of the day. This effectively put two-thirds of the city under German control.[82]
Fighting in the city began to wind down on 14 March. The day was spent with Leibstandarte clearing the remnants of Soviet resistance, pushing east along a broad front. By the end of the day, the entire city was in German hands.[83] Despite the declaration that the city had fallen, fighting continued on 15 and 16 March, as German units cleared the remnants of resistance in the tractor works factory complex, in the southern outskirts of the city.[84]
Aftermath
The German Donets Campaign cost the Red Army fifty-two divisions,[85] including over 70,000–80,000 personnel losses. Of these troops lost, an estimated 45,200 were killed or went missing, while another 41,200 were wounded.[86][87] Between April and July 1943, the Red Army took its time to rebuild its forces in the area and prepare for an eventual renewal of the German offensive, known as the Battle of Kursk.[88] Overall German casualties are more difficult to come by but clues are provided by examining the casualties of the SS Panzer Corps, taking into consideration that the elite Waffen-SS divisions were frequently deployed where the fighting was expected to be the harshest. By 27 March, it is estimated that the SS Panzer Corps had lost around 44% of its fighting strength, including around 160 officers and about 4,300 enlisted personnel.[45]
As SS Panzer Corps began to emerge from the city, they engaged Soviet units positioned directly southwest of the city, including the 17th NKVD Brigade, 19th Rifle Division and 25th Guards Rifle Division. Attempts by the Red Army to re-establish communication with the remnants of the 3rd Tank Army continued, although in vain. On 14–15 March these forces were given permission to withdraw to the northern Donets River.[89] The Soviet 40th and 69th armies had been engaged since 13 March with the Grossdeutschland Panzer grenadier division, and had been split by the German drive.[90] After the fall of Kharkov the Soviet defense of the Donets had collapsed,[91] allowing Manstein's forces to drive to Belgorod on 17 March,[92] and take it by the next day.[91] However, weather and exhaustion forced Manstein's counterstroke to end soon thereafter,[93] despite the Field Marshal's ambitions to also attack the Kursk salient which had been created as a result of the recapture of Kharkov and Belgorod.[75]
Following the German success at Kharkov, Hitler was presented with two options. The first, known as the "backhand method" was to wait for the inevitable renewal of the Soviet offensive and conduct another operation similar to that of Kharkov — allowing the Red Army to take ground, extend itself and then counterattack and surround it. The second, or the "forehand method", encompassed a major German offensive by Army Groups South and Center against the protruding Kursk salient. Ultimately, Hitler chose the "forehand method", which led to the Battle of Kursk.[94]
See also
- First Battle of Kharkov
- Second Battle of Kharkov
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Glantz (1995), p. 296
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Glantz (1991), pp. 252–253
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 McCarthy & Syron (2002), p. 180
- ↑ Cooper (1978), p. 451
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Glantz (1995), p. 141
- ↑ McCarthy & Syron (2002), pp. 177–178
- ↑ McCarthy & Syron (2002), p. 177
- ↑ Megargee (2000), p. 193
- ↑ Cooper (1978), pp. 451–452
- ↑ Cooper (1978), p. 270
- ↑ Cooper (1978), p. 452
- ↑ McCarthy & Syron (2002), p. 178
- ↑ Glantz (1995), p. 143
- ↑ Glantz (1999), p. 10
- ↑ Glantz (1995), pp. 143–144
- ↑ Glantz (1995), p. 144
- ↑ McCarthy & Syron (2002), pp. 178–179
- ↑ McCarthy & Syron (2002), p. 179
- ↑ Krause & Phillips 2005, pp. 162–163
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Glantz (1996), p. 125
- ↑ Glantz (1999), p. 11
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Glantz (1996), p. 124
- ↑ Glantz (1995), p. 145
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Glantz (1996), p. 128
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Glantz (1995), p. 146
- ↑ Glantz (1995), pp. 145–146
- ↑ Glantz (1996), p. 132
- ↑ Glantz (1996), p. 133
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 McCarthy & Syron (2002), pp. 179–180
- ↑ Glantz (1995), p. 147
- ↑ Glantz (1995), p. 303
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 von Mellenthin (1956), p. 252
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 33.3 McCarthy & Syron (2002), p. 181
- ↑ Glantz (1999), p. 15
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 Glantz (1999), p. 16
- ↑ Clark (1965), p. 294
- ↑ Clark (1965), p. 297
- ↑ Glantz (1999), pp. 16–17
- ↑ Slaughterhouse, p. 393
- ↑ Glantz (1999), pp. 17–18
- ↑ Clark (1965), p. 304
- ↑ Slaughterhouse, p. 163
- ↑ Slaughterhouse, p. 165
- ↑ Slaughterhouse, p. 167
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Reynolds (1997), p. 10
- ↑ Slaughterhouse, p. 301
- ↑ Slaughterhouse, p. 304
- ↑ Glantz (1996), p. 126
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 182
- ↑ Glantz (1991), pp. 185–186
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 18
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 Thompson (2000), p. 8
- ↑ Sikes (1988), pp. 8–9
- ↑ Margry (2001), pp. 18–19
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 Margry (2001), p. 19
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 186
- ↑ Glantz (1991), pp. 186–188
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 188
- ↑ Glantz (1991), pp. 188–189
- ↑ Glantz (1996), pp. 130–133
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 189
- ↑ Sikes (1988), p. 9
- ↑ Glantz (1991), pp. 189–191
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 Glantz (1991), p. 191
- ↑ Sikes (1988), pp. 9–10
- ↑ Margry (2001), pp. 19–20
- ↑ Glantz (1996), pp. 133–134
- ↑ von Manstein (1982), p. 432
- ↑ von Manstein (1982), p. 433
- ↑ Glantz (1996), pp. 134–135
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 Margry (2001), p. 20
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 195
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 197
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 199
- ↑ 75.0 75.1 von Manstein (1982), p. 436
- ↑ Margry (2001), pp. 20–22
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 22
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 25
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 27
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 30
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 35
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 36
- ↑ Thompson (2000), p. 11
- ↑ Margry (2001), p. 39
- ↑ Thompson (2000), pp. 11–12
- ↑ Glantz (1995), p. 296; this figure includes personnel losses between February and 25 March 1943.
- ↑ McCarthy & Syron (2002), pp. 180–181
- ↑ Glantz (1999), p. 28
- ↑ Glantz (1991), p. 203
- ↑ Glantz (1991), pp. 203–205
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 Margry (2001), p. 40
- ↑ Glantz (1996), pp. 135–136
- ↑ Glantz (1996), p. 137
- ↑ Cooper (1978), p. 456
References
- Clark, Alan (1965). Barbarossa: The Russian-German Conflict, 1941-1945. New York City, New York: William Morrow. ISBN 0-688-04268-6.
- Cooper, Matthew (1978). The German Army 1933-1945. Lanham, Maryland: Scarborough House. ISBN 0-8128-8519-8.
- Glantz, David M. (1991). From the Don to the Dnepr: Soviet Offensive Operations, December 1942 - August 1943. Routledge. ISBN 0714640646.
- Glantz, David M. (January 1996). "Soviet Military Strategy During the Second Period of War (November 1942–December 1943): A Reappraisal". The Journal of Military History (Society for Military History) 60 (1): 35.
- Glantz, David M.; Jonathan House (1999). The Battle of Kursk. Lawrence, Kansas: Kansas University Press. ISBN 0-7006-0978-4.
- Glantz, David M.; Jonathan House (1995). When Titans Clashed: How the Red Army Stopped Hitler. Lawrence, Kansas: Kansas University Press. ISBN 0-7006-0717-X.
- Heiber, Helmut; David M. Glantz (2003). Hitler and his Generals: Military Conferences 1942 - 1945. New York City, New York: Enigma Books. ISBN 1-929631-09-X.
- Krause, Michael; Cody Phillips (2005). Historical Perspectives of the Operational Art. Washington, United States: Government Printing Office. ISBN 978-0-1607-2564-7.
- Margry, Karel (2001). The Four Battles for Kharkov. London, United Kingdom: Battle of Britain International Ltd.
- McCarthy, Peter; Mike Syryon (2002). Panzerkieg: The Rise and Fall of Hitler's Tank Divisions. New York City, New York: Carroll & Graf. ISBN 0-7867-1009-8.
- Megargee, Geoffrey P. (2000). Inside Hitler's High Command. Lawrence, Kansas: Kansas University Press. ISBN 0-7006-1015-4.
- Reynolds, Michael (1997). Steel Inferno: I SS Panzer Corps in Normandy. New York City, New York: Sarpedon. ISBN 1-885119-44-5.
- Sikes, James E. (29 April 1988). Kharkov and Sinai A Study in Operational Transition. School of Advanced Military Studies, US Command & General Staff College. pp. 86.
- Slaughterhouse: The Encyclopedia of the Eastern Front. The Military Book Club. 2002. ISBN 0-7394-3128-5.
- Thompson (Lt. Col.), Thomas A. (2000). Field Marshal Erich von Manstein and the Operational Art at the Battle of Kharkov. U.S. Army War College. pp. 15.
- von Manstein, Erich (1982). Lost Victories: The War Memoirs of Hitler's Most Brilliant General. St. Paul, MN: Zenith Press. ISBN 0760320543.
- von Mellenthin, F. W. (1956). Panzer Battles. New York City, New York: Ballantine Books. ISBN 0-345-32158-8.
Further reading
- Restayn, Jean (15 January 2000). The Battle for Kharkov, Winter 1942/1943. Canada: Fedorowicz. pp. 450. ISBN 978-0921991489.
- Nipe, George (March 2002). Platz der Leibstandarte: A Photo Study of the SS-Panzer-Grenadier-Division "Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler" and the Battle for Kharkov January-March 1943. Canada: RZM Publishing. pp. 250. ISBN 978-0965758420.
- Nipe, George (1 January 2000). Last Victory in Russia: The SS-Panzerkorps and Manstein's Kharkov Counteroffensive — February-March 1943. Schiffer Publishing. pp. 300. ISBN 978-0764311864.
- Mawdsley, Evan (2005). Thunder in the East: the Nazi-Soviet War, 1941-1945. Hodder Arnold. pp. 502. ISBN 0-340-80808-X.